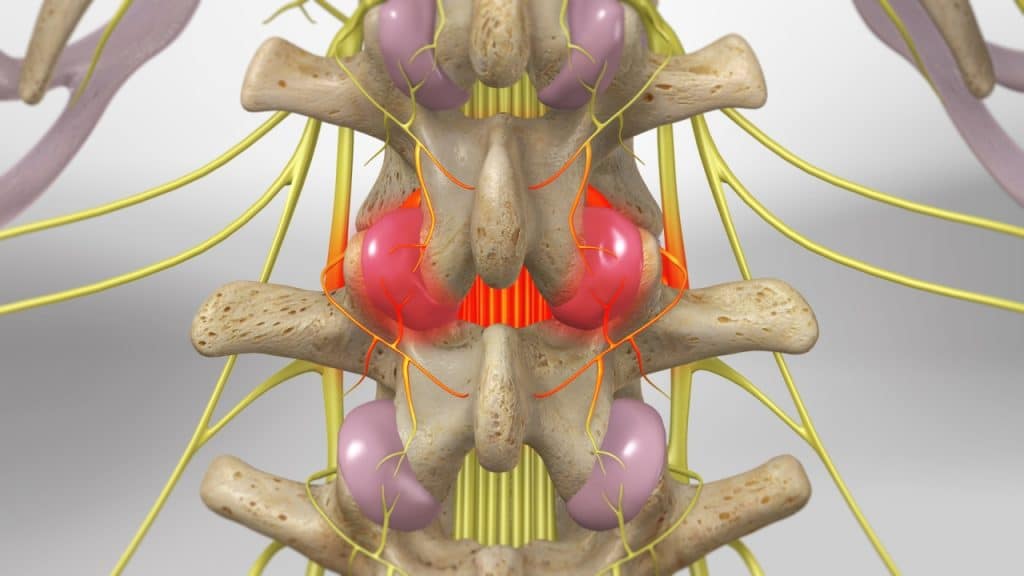
The facet joints or zygapophyseal joints are a set of joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. The lumbar facet joints provide support, stability and mobility to the lumbar vertebrae, especially on extending, bending and rotation of the low back area. Similar to other joints in the body, these joints are vulnerable to inflammation and degeneration. The lumbar medial branch nerves are very small nerves that supply the facet joints in the lumbar spine. They transmit pain signals from the facet joints to the brain. These nerves hurt when facet joints are injured or diseased.
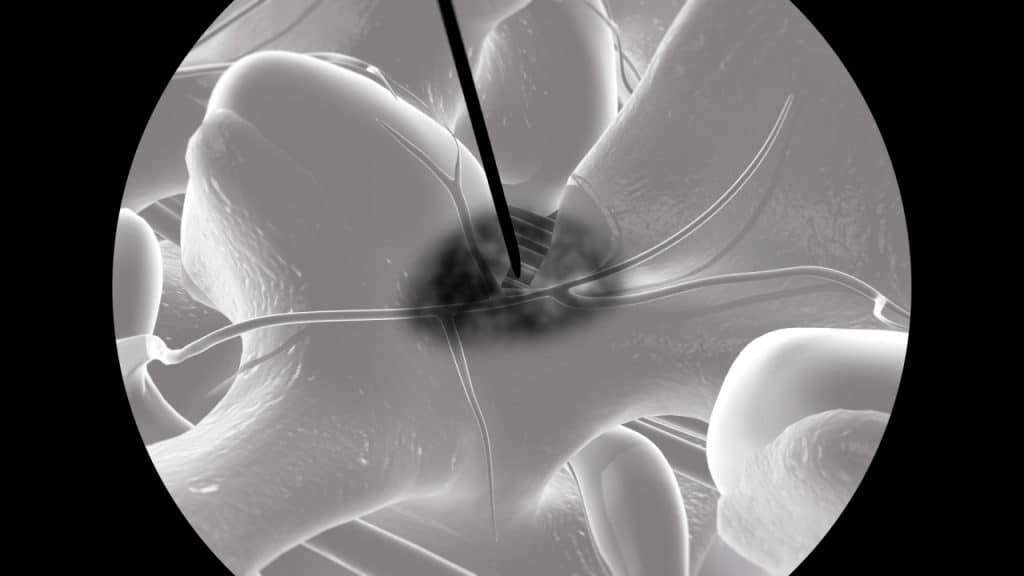
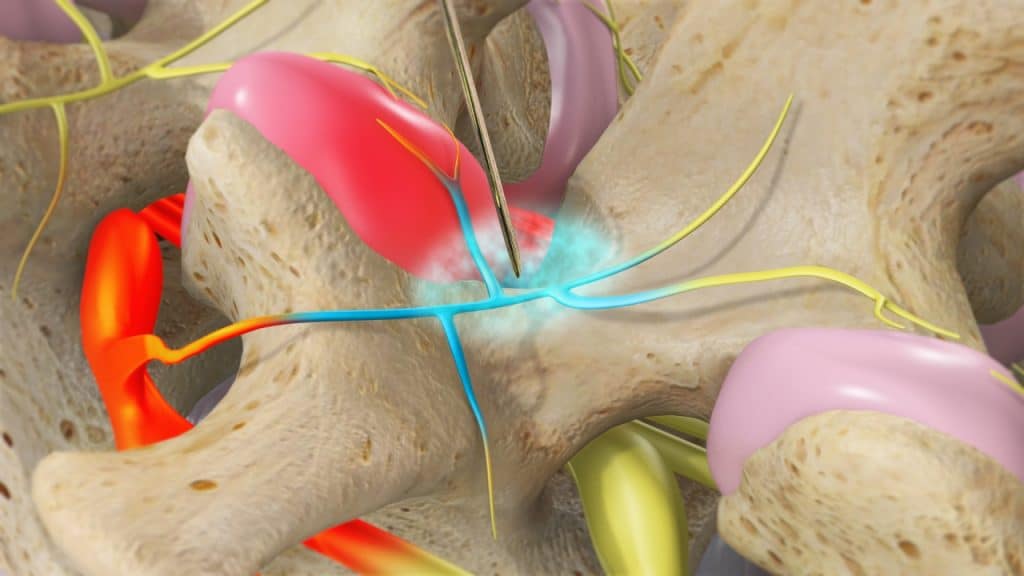
A lumbar medial branch nerve block is a diagnostic procedure using X-ray guidance in which a local anaesthetic is injected very close to the small medial branch nerves connected to a specific facet joint. Lumbar medial branch nerve blocks are used to test if a patient’s pain originates from a given lumbar facet joint. For that purpose, the two nerves that innervate the joint are anaesthetized.
References
- Theodoridis T., Kraemer J.: Injektionstherapie an der Wirbelsäule. Manual und Atlas. 3. Auflage. Thieme 2017.
- Bogduk N.: Practice Guidelines for Spinal Diagnostic and Treatment Procedures. 2. Edition. International Spine Intervention Society 2013.